Contents
0.Recover Binary Search Tree
Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped by mistake.
Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Note:
A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
1.什么是Binary Search Tree?
可以看下这篇文章: 《Binary Search Tree 二叉搜索树 C++》 。二叉搜索树的左节点比根节点要小,右节点比根节点要大。这样利于搜索。
一个典型的二叉搜索树如下:

2.Recover Binary Search Tree 这题目是什么意思?
Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped by mistake.
Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Note:
A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
大致意思是说两个节点的位置调换错了,比如上面的二叉搜索树,2跟5错误调换后变成了下面的样子:
根据二叉搜索树的定义,这样就是非法的二叉搜索树了。
3.如何遍历二叉搜索树
先不管上面题目的解法,二叉搜索树的遍历大致有四种方式。分别是:先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、广度优先遍历。还分递归和非递归方式,我们这里先考虑递归的方式,比较简单。去维基百科摘了一段:
3.1先序遍历
指先访问根,然后访问孩子的遍历方式,其C代码如下:
void XXBL(tree* root){
//Do Something with root
if(root->lchild!=NULL)
XXBL(root->lchild);
if(root->rchild!=NULL)
XXBL(root->rchild);
}3.2中序遍历
指先访问左(右)孩子,然后访问根,最后访问右(左)孩子的遍历方式,其C代码如下
void ZXBL(tree* root){
if(root->lchild!=NULL)
ZXBL(root->lchild);
//Do Something with root
if(root->rchild!=NULL)
ZXBL(root->rchild);
}3.3后序遍历
指先访问孩子,然后访问根的遍历方式,其C代码如下
void HXBL(tree* root){
if(root->lchild!=NULL)
HXBL(root->lchild);
if(root->rchild!=NULL)
HXBL(root->rchild);
//Do Something with root
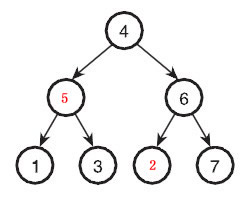
}代码看起来好像这三种方式都一样,是不一样的!以下面这颗树为例。
我们分别打印出遍历时的值:

先序遍历:

中序遍历:

后序遍历:
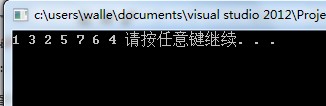
因为二叉搜索树的特点,导致了中序遍历的时候,会是一个递增的效果。
所以我们这道题目的Key就是用中序遍历,就变成了 一个递增的数组中,有两个值调换。1,2,3,4,5,6,7 变成 1,5,3,4,2,6,7。 来复原的问题。
4. 题解
例子:1,5,3,4,2,6,7
大致策略如下:
1.每次我们记录下前一个元素,如果当前节点的值比前一个值要小,说明我们就找到了第一个错误节点的位置。我们的例子中就是3比5小,5就是第一个错误的节点。
2.然后继续往下搜索,第一个比“第一个错误节点”要大的节点的前节点就是第二个错误的节点。我们的例子中6比5大,所以2就是第二错误的节点。
代码如下:
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* preNode = NULL;
TreeNode* firstWrongNode = NULL;
TreeNode* secondWrongNode = NULL;
void ZXBL(TreeNode* root){
if(root->left != NULL){
ZXBL(root->left);
}
//找到第一个错误节点
if(preNode != NULL && firstWrongNode == NULL && preNode->val > root->val){
firstWrongNode = preNode;
}
//找到第二个错误节点
if(firstWrongNode != NULL && secondWrongNode == NULL && root->val > firstWrongNode->val){
secondWrongNode = preNode;
}
//都找就退出
if(firstWrongNode != NULL && secondWrongNode != NULL){
return;
}
//每次都把上一个节点记录下来
preNode = root;
if(root->right != NULL){
ZXBL(root->right);
}
}
void recoverTree(TreeNode *root) {
ZXBL(root);
//树只有两个节点时,要这样考虑
if(secondWrongNode == NULL){
secondWrongNode = preNode;
}
//调换两个错误节点的值,就复原了二叉搜索树
swap(firstWrongNode->val, secondWrongNode->val);
}
};http://www.waitingfy.com/archives/990
Tags: Binary Search Tree
990

